Kren-M: Meghalaya's First Foundational AI Model for the Khasi Language
The First Indigenous Language Model from Northeast India
Kren-M is Meghalaya’s first foundational AI model and the first generative language model built for the Khasi language. Developed by MWire Labs in Shillong, Kren-M represents a major step forward for Indigenous NLP, enabling high-quality Khasi chat, translation, summarization, and domain-specific conversational AI.
Unlike generic multilingual models, Kren-M is trained on Khasi, for Khasi. It uses custom tokenization, clean corpus engineering, and a carefully designed CPT–SFT pipeline to achieve production-ready performance, scalable for government services, enterprise applications, and public use.
This launch establishes Meghalaya as a new AI hub in Northeast India, setting the foundation for a broader regional language AI ecosystem
Why the Khasi Language Needs Its Own AI Model
The Challenge for Low-Resource Languages
Most large language models fail to handle Khasi properly because:
- Tokenization inefficiency: Khasi words are broken into many subwords, wasting context and reducing fluency.
- No high-quality corpus: Public datasets contain contamination, code-mixing, and noise.
- Bilingual instability: Generic models auto-translate English prompts, echo instructions, or mix languages unpredictably.
- Limited academic focus: Northeast Indian languages are rarely included in multilingual benchmarks or foundational model research.
These issues block Khasi speakers from benefiting fully from generative AI.
Introducing Kren-M
Meghalaya’s First Foundational AI Model
Kren-M solves these challenges using a fully customized approach:
- 2.6B-parameter bilingual model built on Google’s Gemma-2-2B architecture.
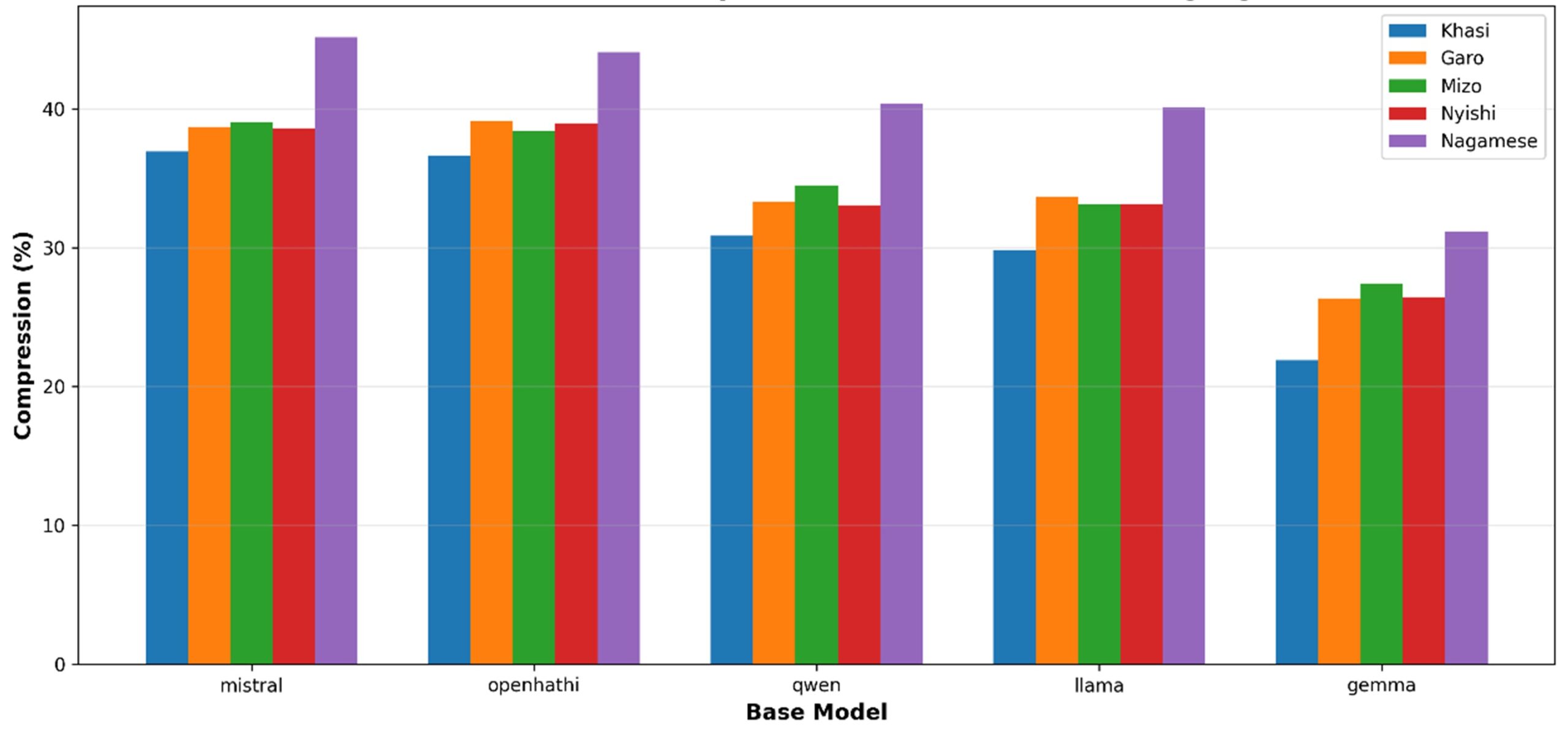
- 2,135 custom Khasi–Garo tokens added via SentencePiece vocabulary extension.
- 30–36% token efficiency improvement compared to Gemma-2-2B baseline.
- 5.43 million cleaned Khasi-language corpus for continued pre-training.
- 33,034 supervised instruction examples in Khasi chat, English chat, and translation.
- Response-aware SFT that eliminates auto-translation and echoing.
Technical Foundations
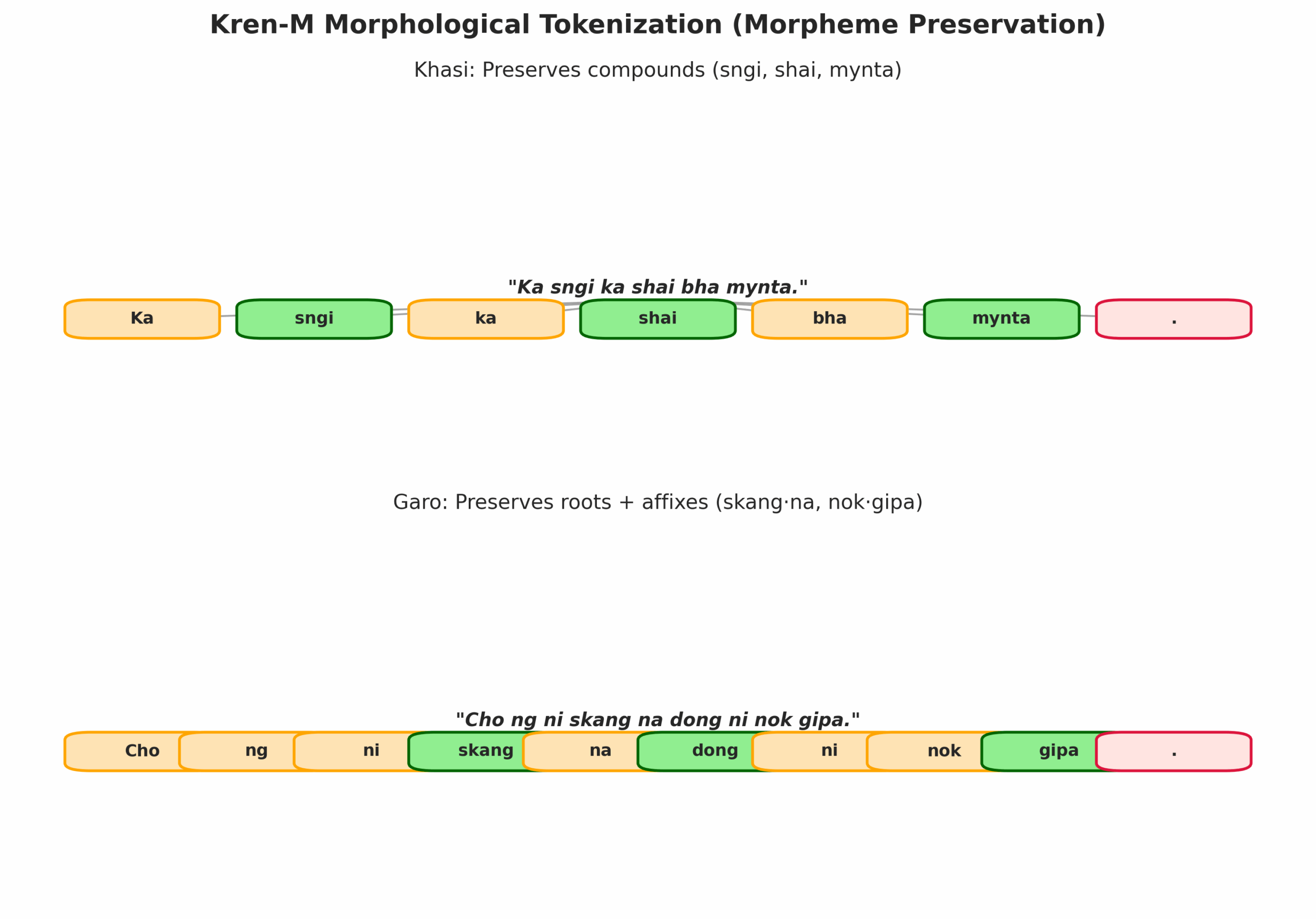
1. Custom Tokenizer for Khasi, Garo & the Northeast
We trained a specialized tokenizer to fix over-segmentation:
- 66,188 sentences (Khasi + Garo)
- 5,000-token SentencePiece model
- 2,135 new tokens added to Gemma’s base vocabulary
- 30–36% fewer tokens per Khasi/Garo sentence
- Accuracy improves because the model sees complete Khasi/Garo morphemes
Kren-NE Tokenizer (New!)
MWire Labs now maintains Kren-NE, an expanding tokenizer project covering:
- Khasi
- Garo
- Mizo
- Assamese
- Manipuri (Meitei)
- Nagamese
- Nyishi
This positions Kren-NE as the first multi-language tokenizer for Northeast India, enabling future models beyond Kren-M.
2. Continued Pre-Training (CPT) — Clean Data First
We curated the largest Khasi text corpus to date:
- 5,433,041 sentences
- Removed HTML noise, verse citations, ellipses, auto-generated spam, mixed-script anomalies
- Two-stage CPT:
- Stage 1 (LR 2e-4): Validation loss → 2.974 (from 6.77 baseline)
- Stage 2 (LR 1e-4): Minor refinement
Result:
45.5% improvement in validation loss
Fluent Khasi generation with minimal artifacts.
3. Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT)
We built a highly selective bilingual dataset:
- 10,097 Khasi translation pairs
- 15,000 English Dolly-style instruction pairs
- 7,937 Khasi conversational pairs
Critical fixes:
- Removed 9,903 implicit translations
- Implemented response-only loss masking
- Enforced EOS token at every sample
- Trained embed_tokens + lm_head for new vocabulary activation
Final SFT model loss: 0.85
Evaluation & Examples
Even without heavy RLHF, Kren-M performs strongly:
Khasi Chat (Native Fluency)
User: Kumno phi long?
Kren-M: Nga biang. Phi kumno?
English Chat (No auto-translation)
User: “I need help with my homework.”
Kren-M: “Sure! What subject are you working on?”
Khasi Translation
Input: “Translate to Khasi: How are you?”
Output: Kumno phi long?
Why Kren-M Matters for Meghalaya
Transforming Digital Services
- Government communication assistants
- Local-language chatbots for departments
- Automatic Khasi summarization for public-policy documents
- Tourism chatbots for Shillong / Sohra
- Agricultural advisory chatbots in Khasi
- Local support centers, BPOs, helplines
Empowering Businesses
- Local call centers with Khasi AI agents
- Enterprise chatbot automation
- Custom domain fine-tuning
- On-prem security for sensitive work
Cultural & Linguistic Preservation
Kren-M is a step toward protecting and modernizing Khasi language digitally, ensuring Indigenous languages do not get left behind.
*Kren-M is trained on a curated mix of publicly available text, licensed data, and MWire Labs’ proprietary datasets
Quick start
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("MWirelabs/Kren-M", torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("MWirelabs/Kren-M")
prompt = "<start_of_turn>user\nTranslate to Khasi: Hello, how are you?<end_of_turn>\n<start_of_turn>model\n"
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=False)
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
Let's Build Together
Are you a researcher, developer, or part of a language community in Northeast India? We are always looking for partners to collaborate on new datasets, fine-tune models, and advance the state of regional AI.